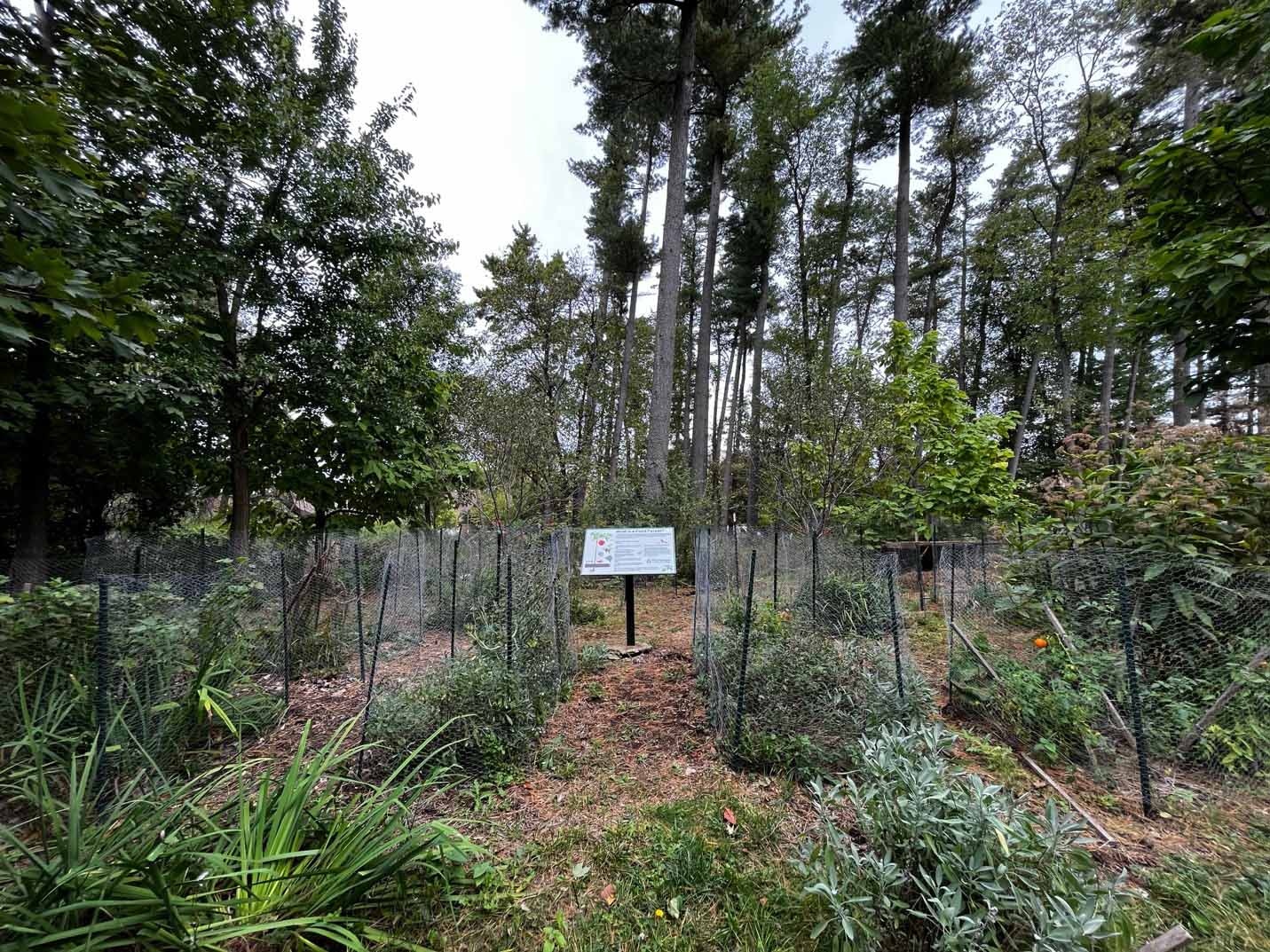
Wide angle photo of the WCC Food Forest. Photo Credit: Karlos Madrigal
What a Food Forest is
A food forest is a type of permaculture gardening practice that attempts to mimic the ecosystems naturally found in forests. Permaculture means it’s a natural system to manage agriculture, in this case with a structure like a native forest. We try to plant native perennial species while experimenting with our favorite annuals. Perennials are plants like coneflower (Echinacea purpurea) that, once planted, come up year after year. Annuals are plants like corn (Zea mays) that have to be planted each year.
There are generally seven layers of a Food Forest: the canopy, the sub canopy, the shrub layer, the herbaceous layer, the root layer, the ground cover layer, and the vine layer. Some Food Forest even have an eighth layer, called the mycelial or fungal layer. The purpose of all these layers is for each to provide food while also providing the usual services to the forest ecosystem. In addition, the Food Forest sequesters carbon, helping to mitigate climate change.
The Layers
- The canopy layer (shagbark hickory and mulberry trees) and the sub-canopy layer (apple trees) provide shade for the layers below while providing food like nuts and berries for humans. They also provide food and habitat for animals like birds, squirrels, deer, and insects.
- The shrub layer (currant and elderberry bushes, f) attracts pollinators while the elderberry plants help increase nitrogen levels in the soil. They both provide berries for humans and food and habitat for other animals.
- The herbaceous layer (sage, anise hyssop) holds soil as a cover crop and can improve soil if used as mulch. Again, the layer provides food (herbs) for humans and food and habitat for other animals.
- The ground cover layer (strawberries) protects the soil from erosion and keeps weeds from growing. This layer also provides berries for humans and food and habitat for other animals.
- The root layer (compass plant) has roots or tubers that bring nutrients from deep in the soil. Native plants like the compas plant provide food and habitat for animals.
- The fungal layer (shitake and oyster mushrooms) includes edible mushrooms that are planted in order to help with decomposition and recycling of nutrients.
- The vine layer– we do not currently have a planted vine layer.
Native Plants Support Native Animals
We try to plant native plants wherever possible in order to support native insects, which in turn feed native birds like bluebirds and black-capped chickadees. Put another way, native plants in our gardens and forests support our favorite songbirds!
Why is There One at WCC?
The Food Forest at WCC was established in 2019 by the Students for Sustainability Club and Sustainability Literacy Task Force (SLTF), with help from the WCC Grounds Department. It was designed by students to help feed students, improve food resiliency in the area, and prevent climate change. Many of the plants in the Food Forest are native to Michigan. WCC was built on what was originally an apple orchard and was indigenous territory before that.
What Is in the Food Forest, How We Plant Seeds and Grow Leaders
There are seven beds of plants in the Food Forest, all with a variety of plants. Some of the prized native plants that produce food for humans are apple trees, strawberries, currants, elderberries, serviceberries and a hickory (nut) tree. Other plants include annuals like onions, garlic, tomatoes, squash, kale, beans, corn, and oregano.
The Food Forest is primarily taken care of by the Students for Sustainability Club here at Washtenaw and is supported by the Sustainability Literacy Task Force (SLTF). Students develop leadership skills as they take on projects like planting, weeding, watering, pruning and Food Forest design. Student volunteers also build speaking skills as they conduct tours in the Food Forest and lead workshops.
Where are Other Food Forests
Other Food Forests in Washtenaw County can be found at Buhr Park and at Leslie Park. They are both open to the public and have a wide variety of plants.
Conclusion
Food Forests are planted to increase food supplies for humans and for native animals. Remember that it is important to try and plant as many native plants as possible. They can be easier to maintain, and they enhance native food chains and ecosystems. Here is some local information on native plants and places to buy them. Many of the plants can provide habitats for wildlife like bees or birds. Also remember to be pollinator aware and leave some bare soil and refuse in the garden for insects that are overwintering. Refuse includes things like leaves, brush piles, fallen logs, and plant stems.
Things You Can Do To Learn More and Make a Difference
- visit or volunteer in a Food Forest
- plant native species in your yard
- practice pollinator-aware yard care, leaving leaves, brush, plant stems and bare dirt to help native insects overwinter
Sources
Tags: Sustainability